Hoshin Kanri – Strategy Development and Deployment
What is Hoshin Kanri Strategy Development and Deployment? How how does this method work in implementation?
Within the framework of lean management, there are numerous tools and methods that help companies increase their efficiency and competitiveness. One of these methods is Hoshin Kanri, a strategic planning technique that helps companies define, implement and monitor their goals.
We take a closer look at Hoshin Kanri and its importance for strategy development in companies.
What is Hoshin Kanri?
What is Hoshin Kanri – Strategy Development and Deployment? Hoshin Kanri, also known as Policy Deployment, is a systematic method for developing and implementing strategies. The term “Hoshin” means “direction” or “compass needle” in Japanese, while “Kanri” stands for “management.” Hoshin Kanri enables companies to link their strategic goals with the operational activities and individual goals of their employees. It creates a clear alignment and a common focus on achieving the company’s goals.

Principles of Hoshin Kanri – Strategy Development and Deployment
Hoshin Kanri – Strategy Development and Deployment is based on some fundamental principles:
- Hoshin planning: Corporate goals and strategies are clearly defined and communicated at all levels of the company. This creates a common understanding and commitment to achieving goals.
- Breakthrough Goals: Hoshin Kanri places special emphasis on identifying breakthrough goals. These are challenging and transformative goals that enable the company to achieve significant improvements and gain competitive advantage.
- North Star: All important breakthrough targets are summarized in the so-called “North Star”. A key performance indicator (KPI) is defined for each target. The various KPIS are visualized in a KPI dashboard.
- A3 Strategies: An implementation manager is defined for each breakthrough target including the KPI. This person develops an implementation strategy (A3 strategy) that includes various improvement projects.
- X-Matrix: The X-Matrix is an important tool in Hoshin Kanri. It visualizes the link between the company’s goals, associated key initiatives, responsibilities and performance indicators. This provides a holistic view of the strategy and makes it easier to monitor progress.
- PDCA Cycle: Hoshin Kanri uses the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle for continuous improvement. Planning the strategy goes hand in hand with implementing, reviewing and adjusting the actions to ensure that the goals are achieved.
Hoshin-Kanri Planning process
The Hoshin Kanri planning process includes 7 steps to align strategic goals, identify resources, and develop an execution plan.
- Building an overall strategy consisting of vision, mission, arena, strategic pillars
- Development of breakthrough goals & annual targets/focus targets
- Definition of the North Star & development of a KPI dashboard
- Development of A3 strategies by an implementation manager
- Definition of improvement projects and success factors
- Development of the X-Matrix
- Catch-ball process including action plans
- Weekly operational implementation and deviation management
- Monthly / quarterly evaluation using the bowling chart
- Annual review in the strategy meeting
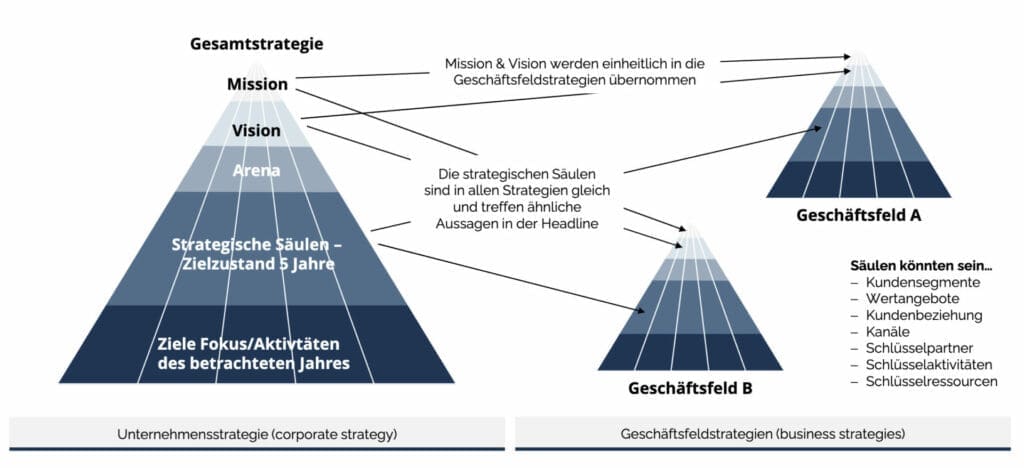
Development of the overall strategy
In the Hoshin-Kanri process, the overall strategy is developed first. The overall strategy includes the mission, vision, arena, strategic pillars and focus goals/activities.

Mission
The mission is timeless and describes the self-image of the company. The mission is to be handled in the same way for all sub-strategies.
Vision
The vision is a statement that gives a comprehensive and a high aiming picture of the future that the company is aiming for. The vision period describes a period of 5-10 years. The company vision is to be handled in the same way for all sub-strategies.
Arena
The arena is the definition of the market, regions and industries in which the company will remain or become active. The arena describes the core value stream or the business model with which the company wants to earn money.
Strategic pillars
Strategic pillars (target state in approx. 5 years) represent fields of action and are defined in terms of their orientation in the company in a uniform and suitable manner for all value streams/business models; e.g. services & products, operational processes, leadership, management & CIP, collaboration & organization, team & qualification.
Focus goals / annual goals
The top 3 focus goals / annual objectives of the year under consideration are defined for each strategic pillar, as well as associated activities.
Overall strategy as company guardrail
Die Gesamt-Strategie wird als erstes festgelegt, um den Teamstrategien die richtige Orientierung zu geben und die Leitplanken zu setzen. Diese Leitlinien gelten dann auch für den Fall, dass die Gesamtstrategie in Geschäftsfeldern weiterentwickelt wird.
Traditional versus team-oriented strategy development
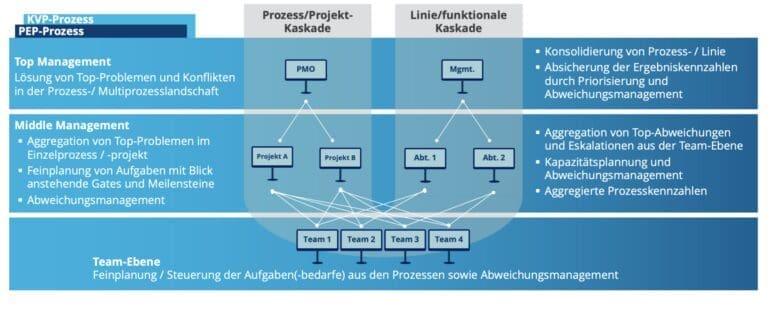
In the traditional implementation of the Hoshin Kanri method, it was a strict top-down target process that was also highly segmented.
Today, the Hoshin Kanri process has been adapted. Before the goals are unfolded vertically in the organization, the horizontal alignment takes place in top management.
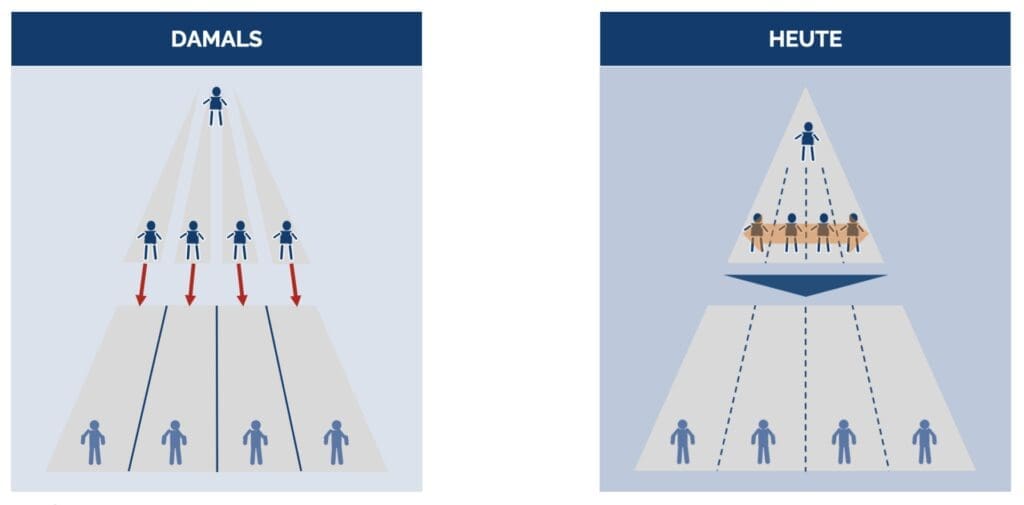
The cross-functional view increases the understanding of all functions for the improvement of the value stream. Through a process of goal alignment during the year, goals are repeatedly coordinated among management team members.

The management team has the common goal of achieving the overall strategy and shares responsibility for the results and tracking of the strategy.
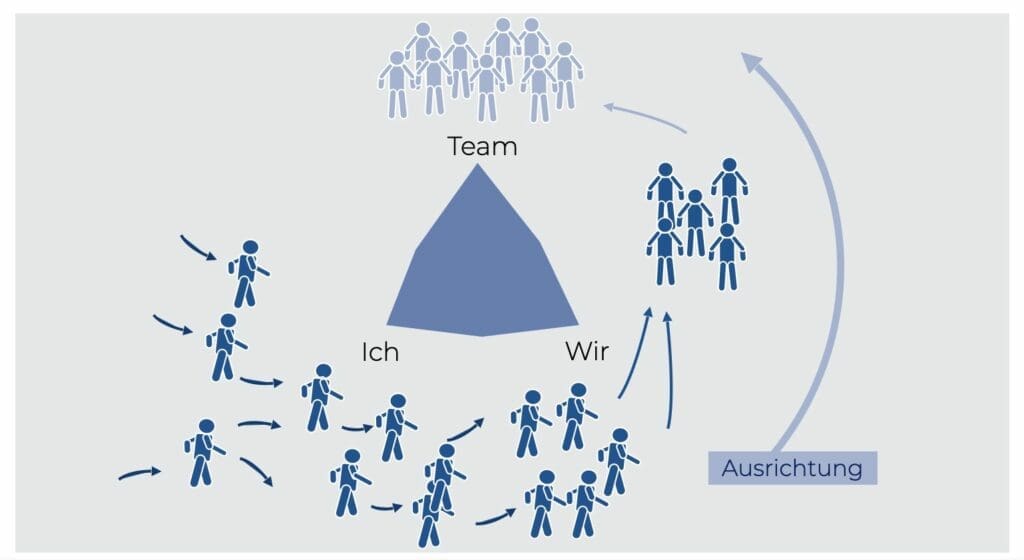
North Star, KPI Dashboard & A3 Strategy
The key breakthrough targets are selected from the overall strategy and summarized in the so-called “North Star”. A key performance indicator (KPI) is defined for each target. The various KPIS are visualized in a clear KPI dashboard. An implementation manager is defined for each breakthrough target including the KPI. This person develops an implementation strategy (A3 strategy) that includes various improvement projects.

X-Matrix
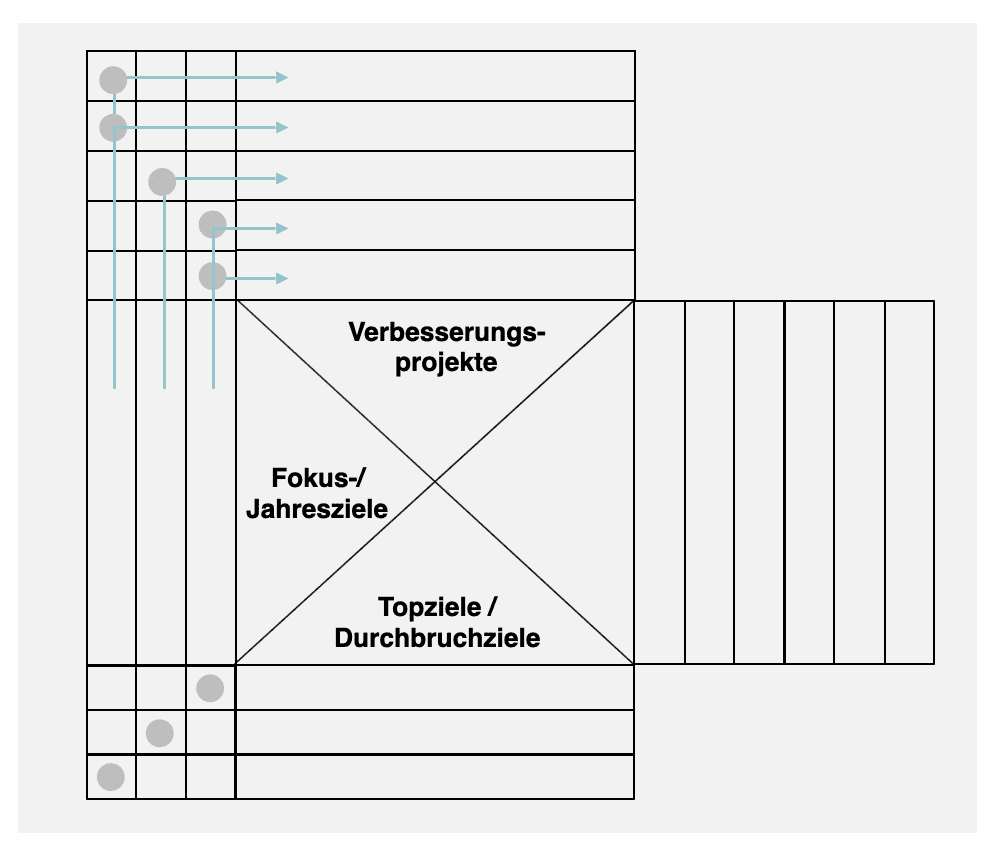
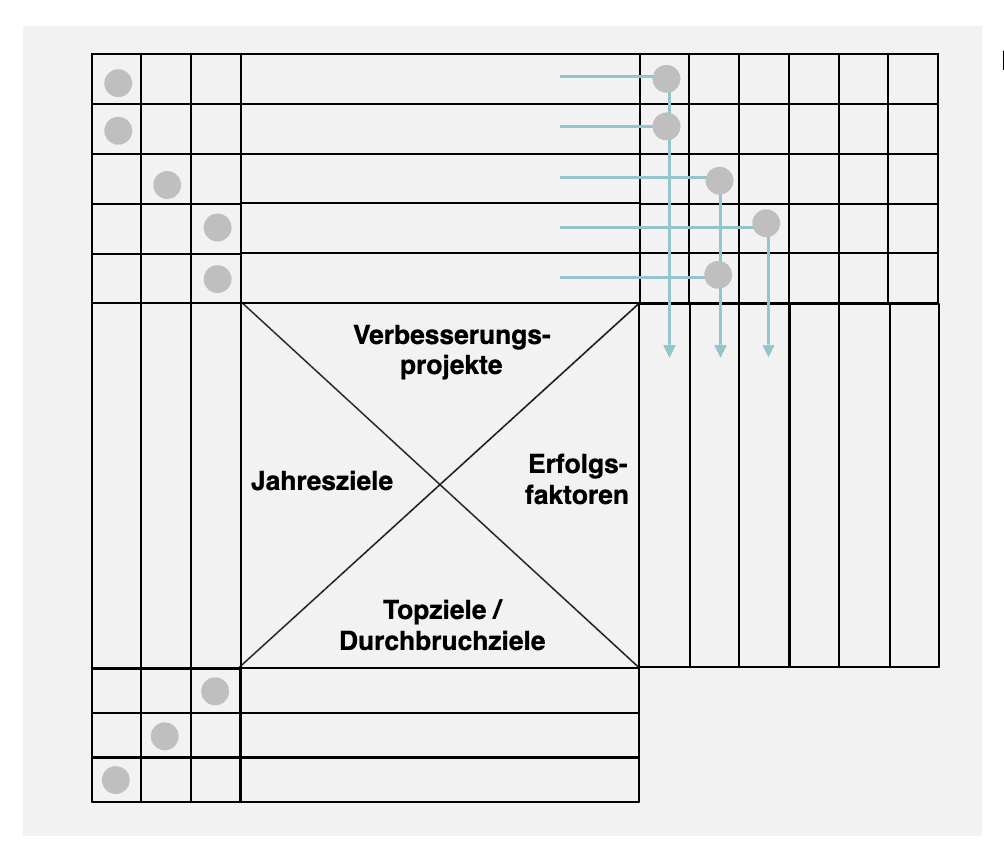
The X-Matrix is an important tool in the Hoshin-Kanri process. In addition to the breakthrough goals (What do we want to achieve?), the annual or focus goals (How far do we want to get this year?) are recorded in the X-Matrix, as well as the respective improvement projects (How do we achieve the goal?) and success factors (“Which project (driver) leads to which success factor (effect)?”. Finally, a responsible person is defined for each topic.
The X-Matrix serves as a control tool for the Hoshin-Kanri process during the year. On the basis of the X-Matrix, the progress of the improvement projects and thus the achievement of objectives is checked and corrected.

Example X-Matrix
In an example we go through the application of the X-Matrix once in the following. The Hoshin planning process has already been completed and the result is that the breakthrough targets run a marathon in less than 4 hours.
In the following illustration, you can see how the annual goals, improvement projects and success factors are listed in the X-Matrix in addition to the breakthrough goal.
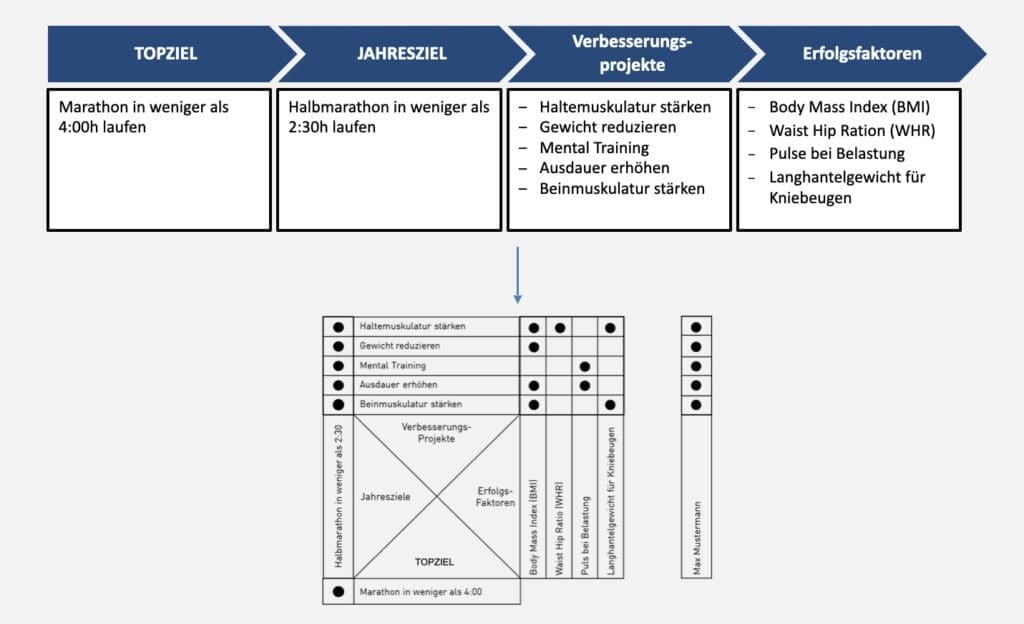
Break breakthrough goals down to focus goals
Breakthrough goals are broken down into lower-level annual goals or focus goals.

Characteristics of annual goals or focus goals
- Define annual targets by proportions of top/breakthrough targets, which have a time horizon of 3-5 years, to be achieved in the following year
- Usually the annual goals have the same metrics as the breakthrough goals
- When 1 breakthrough goal is broken down into 2 annual goals, at least 2 improvement projects become necessary. The more annual targets result, the more improvement projects follow from them
- Annual targets are defined by the upper hierarchy level. E.g. reduction of manufacturing costs by 40% within the next 4 years Reduction of manufacturing costs by 15% in the following year
The improvement projects are derived from the annual goals or focus goals
Features of improvement projects
- Improvement projects are projects designed to achieve one or more annual goals. ” Which project (driver) must be developed to achieve the annual goal?”
- The improvement projects are selected from a project list, which has been created through a driver-impact analysis of the annual objectives
- An action plan is drawn up for each improvement project, in which the individual work packages are defined
- The improvement projects can also be derived from a value stream analysis
Success factors are used to check the degree of implementation of the improvement projects
Properties of success factors
- Deriving success factors uses the question: “Which project (driver) leads to which success factor (effect)?”
- Success factors should not be confused with ordinary key performance indicators – therefore their definition is often not straightforward
- Success factors measure results and are not action plans with milestones
- Success factors are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and timely (SMART)
- Success factors can be broken down into monthly sub-factors
- E.g. improvement of total OEE to 95% by December
The responsible persons are defined for the improvement projects
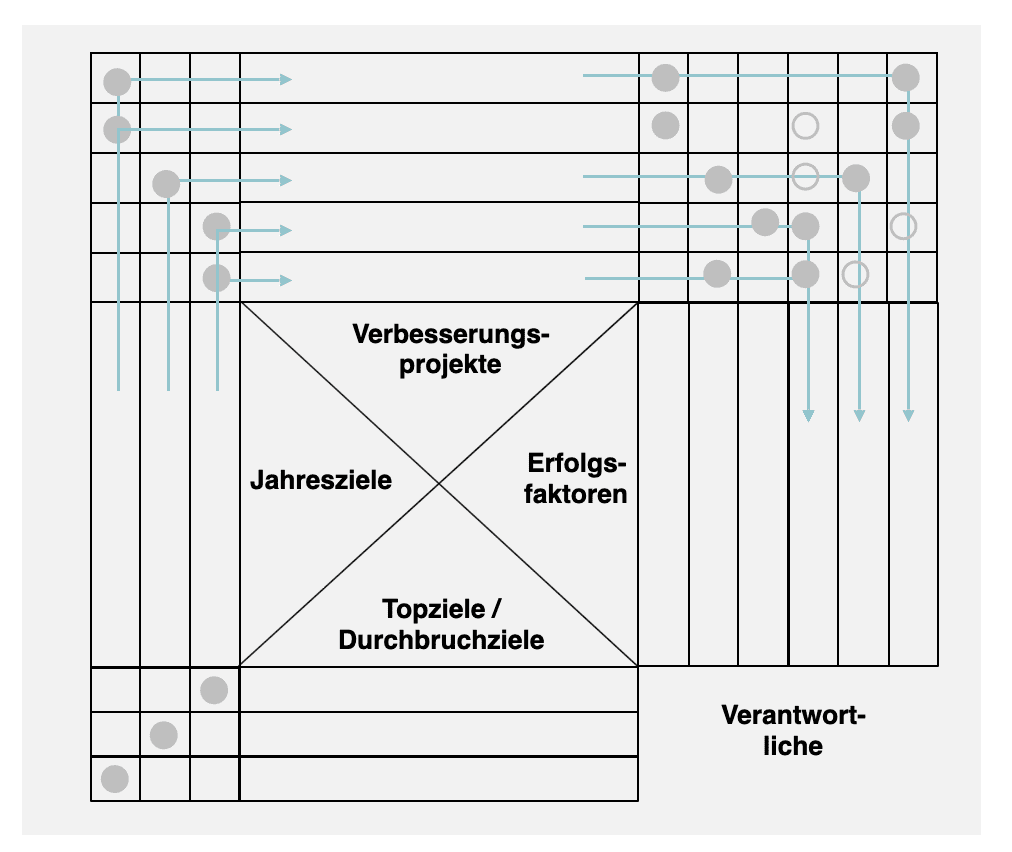
In the X-Matrix, a responsible person (black circle) and, if necessary, further supporting persons (white circle) are defined for each improvement project.
The Catchball-Process
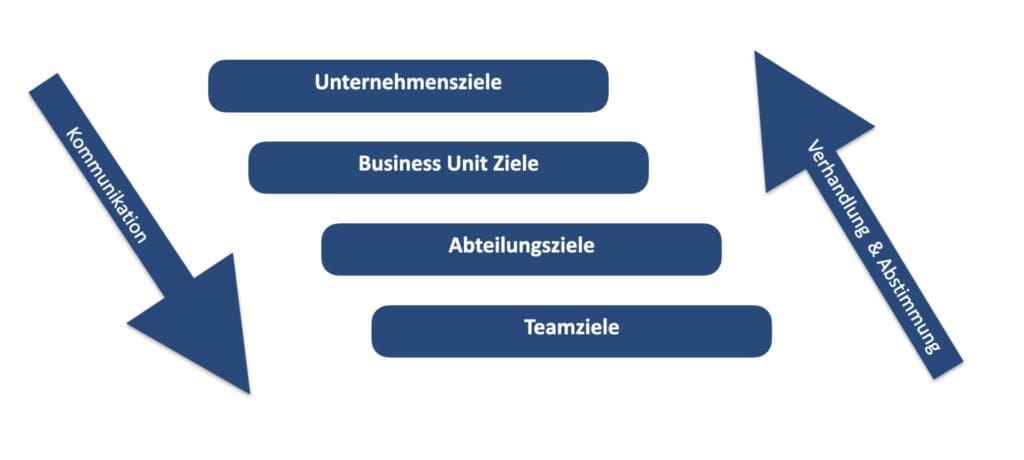
The “catch-ball” process describes the process of target coordination between the company management and the executing teams. The “target ball” is virtually “thrown” to the next level through communication and “caught” there in the context of negotiations & coordination.
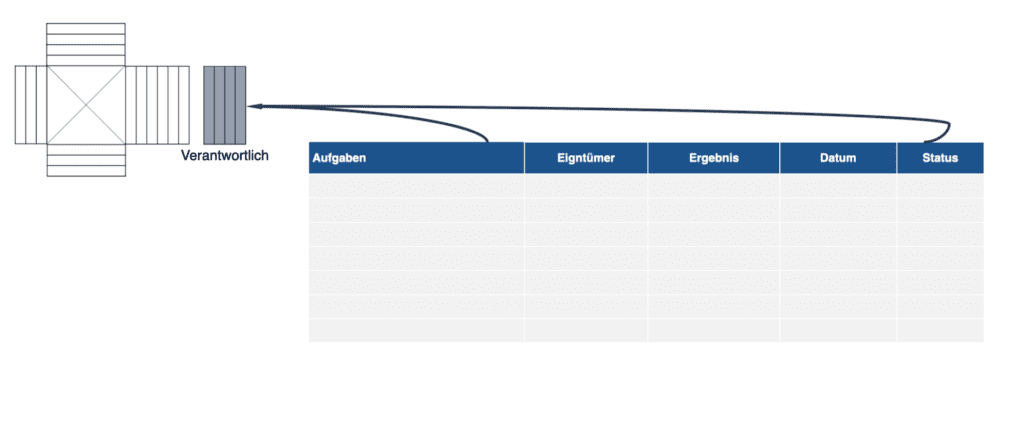
The responsibility matrix supports the assignment of responsibility during the catchball process.
Hoshin Kanri Strategy Development and Deployment: advantages
The application of Hoshin Kanri offers companies numerous advantages:
- Clear alignment: Hoshin Kanri creates a unified focus on corporate goals and improves communication and coordination at all levels.
- Strategic implementation: The method enables companies to effectively put their strategies into action by establishing clear goals, responsibilities and actions.
- Continuous Improvement: By integrating the PDCA cycle, Hoshin Kanri fosters a culture of continuous improvement and enables companies to continually adapt and optimize their strategies and activities.
- Employee Involvement: Hoshin Kanri involves employees at all levels in the strategy development process, encouraging active participation and ownership.
Summary
Hoshin Kanri is a powerful lean management methodology that helps companies clearly define, implement and monitor their strategies. By creating clear alignment and involvement of all employees, Hoshin Kanri helps companies effectively achieve and continuously improve their goals. If you want to take your business to the next level, implementing Hoshin Kanri can be a valuable step.

Contact us now!
We have more than 20 years of experience and deliver high quality consulting for your Agile, Lean or Digital Transformation.